In an increasingly connected world, the demand for efficient and high-speed data communication is greater than ever. While personal and home networks typically rely on Local Area Networks (LANs) and businesses on Wide Area Networks (WANs), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) play a crucial role in connecting networks across broader urban and metropolitan areas. This blog explores the significance of MANs, their key features, and their impact on modern connectivity.
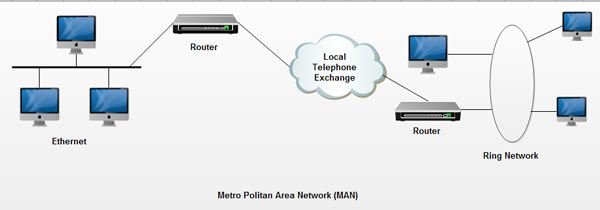
What is a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)?
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a high-speed network that spans a city or metropolitan area, providing connectivity between multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) within that region. Unlike LANs, which are confined to a single building or campus, or WANs, which cover larger geographic areas, MANs bridge the gap between these two types of networks. They offer a solution for organizations and service providers to extend their network reach beyond a single location but within a city or urban area.
Key Features of Metropolitan Area Networks
- Geographic Scope:
- Coverage Area: MANs typically cover areas ranging from a few kilometers to several tens of kilometers. This makes them ideal for connecting multiple buildings, offices, or campuses within a city.
- Infrastructure: They often use a combination of fiber optic cables, microwave links, and leased lines to provide high-speed connectivity across the metropolitan area.
- High-Speed Connectivity:
- Bandwidth: MANs offer higher bandwidth compared to standard LANs, making them suitable for high-data applications like video conferencing, streaming, and large data transfers.
- Speed: With speeds often ranging from 10 Mbps to several Gbps, MANs can handle large volumes of data with minimal latency, ensuring efficient communication between different locations.
- Scalability and Flexibility:
- Expansion: MANs are designed to be scalable, allowing for the addition of new connections and expansion of the network as needed. This flexibility supports the growing needs of urban areas and evolving technology.
- Integration: They can integrate various types of networks, including fiber optics, Ethernet, and wireless technologies, to create a cohesive communication system.
- Cost-Effective Solutions:
- Shared Infrastructure: By utilizing shared infrastructure, MANs can reduce the cost of connecting multiple locations compared to deploying individual connections for each site.
- Service Providers: Many MANs are operated by service providers who offer managed services, reducing the burden on organizations to maintain their network infrastructure.
Applications of Metropolitan Area Networks
- Business Connectivity:
- Multi-Site Organizations: Businesses with multiple offices or branches within a city benefit from MANs by achieving seamless connectivity between locations, enabling efficient data sharing and communication.
- Data Centers: MANs connect data centers and server farms within metropolitan areas, facilitating high-speed data transfer and supporting cloud services and applications.
- Educational Institutions:
- University Networks: Universities and educational institutions often use MANs to connect various campuses and research facilities, supporting collaborative projects, online learning, and resource sharing.
- Government and Public Services:
- Public Safety: MANs support public safety networks by connecting emergency response centers, surveillance systems, and communication hubs within a city.
- City Infrastructure: They can integrate with smart city initiatives, linking various municipal services such as traffic management, utilities, and public transportation systems.
- Telecommunications:
- Internet Service Providers: ISPs use MANs to extend their service coverage within metropolitan areas, providing high-speed internet access to businesses and residential customers.
- Carrier Networks: MANs serve as a backbone for carrier networks, facilitating connectivity between different network segments and enhancing overall network performance.
Benefits of Metropolitan Area Networks
- Enhanced Connectivity:
- Improved Communication: MANs enable fast and reliable communication between different locations within a city, enhancing productivity and collaboration for businesses and organizations.
- High Bandwidth: With high-speed connections, MANs support data-intensive applications and services, ensuring smooth operation and minimal disruption.
- Cost Efficiency:
- Economies of Scale: By leveraging shared infrastructure, MANs reduce the cost of network deployment and maintenance, offering a cost-effective solution for urban connectivity.
- Managed Services: Service providers offer managed MAN solutions, reducing the need for organizations to invest in and maintain their network infrastructure.
- Flexibility and Scalability:
- Adaptability: MANs can adapt to changing needs and technologies, supporting the integration of new services and expansion of network capabilities.
- Future-Proofing: The ability to scale and upgrade ensures that MANs can accommodate future growth and advancements in technology.

Conclusion
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) play a vital role in bridging the gap between local and wide-area connectivity, providing high-speed, reliable, and scalable solutions for urban areas. With their ability to connect multiple locations, support high-bandwidth applications, and offer cost-effective solutions, MANs are essential for businesses, educational institutions, government services, and telecommunications providers. As cities continue to grow and technology evolves, MANs will remain a key component in supporting the connectivity needs of modern urban environments.














