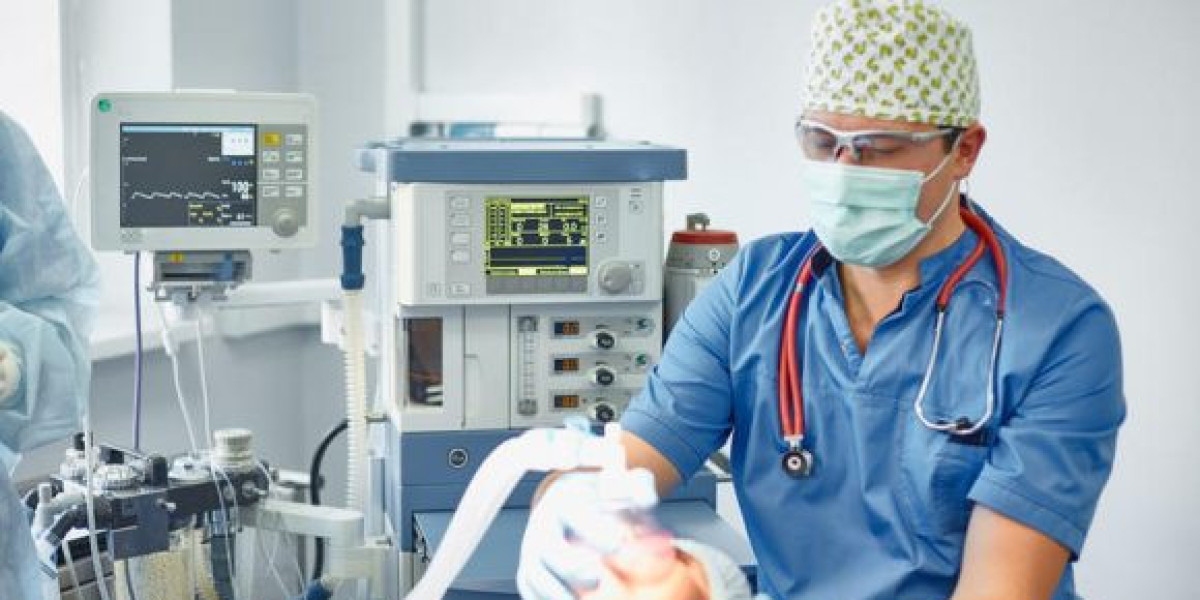
In the world of modern medicine, the role of an anesthetist is both vital and intricate. They are the medical professionals responsible for ensuring that patients remain comfortable, pain-free, and safe during surgeries, diagnostic procedures, and certain therapeutic treatments. While surgeons perform operations, it is the anesthetist who monitors and maintains the patient’s vital functions, manages pain, and ensures a smooth transition into and out of anesthesia. Without their expertise, even the most advanced medical procedures would not be possible.
Understanding the Role of an Anesthetist
An anesthetist is a specialist in the administration of anesthesia, the medical practice of using drugs to prevent pain during surgical and medical procedures. Their responsibilities go far beyond simply “putting a patient to sleep.” Before surgery, they conduct thorough preoperative assessments, reviewing the patient’s medical history, current health status, and any potential risks associated with anesthesia. This evaluation allows them to tailor the anesthesia plan to the patient’s needs, ensuring maximum safety and comfort.
During surgery, an anesthetist continuously monitors vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and breathing patterns. They make real-time adjustments to anesthesia levels, ensuring that the patient remains unconscious or comfortably sedated without complications. After the procedure, the anesthetist manages the patient’s emergence from anesthesia, controlling pain and preventing postoperative side effects such as nausea, dizziness, or breathing difficulties.
Types of Anesthesia Managed by Anesthetists
Anesthetists are skilled in administering different types of anesthesia, each suited for specific medical needs:
General Anesthesia – Used for major surgeries, rendering the patient completely unconscious and pain-free.
Regional Anesthesia – Numbs a larger part of the body, such as spinal or epidural anesthesia, commonly used in childbirth or orthopedic surgery.
Local Anesthesia – Numbs a small area of the body, allowing minor procedures to be performed without discomfort.
Sedation – Keeps the patient relaxed and drowsy, often used for diagnostic tests like endoscopies.
The choice of anesthesia depends on the procedure, the patient’s health condition, and any previous reactions to anesthesia.
Skills and Expertise of an Anesthetist
Anesthetists combine technical knowledge with precise decision-making under pressure. Their expertise includes:
Comprehensive knowledge of pharmacology to select the correct drugs and dosages.
Understanding the body’s physiological responses during surgery.
Quick, critical thinking in emergencies.
Effective communication with surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare professionals.
They also need to be compassionate and reassuring, as many patients feel anxious before undergoing anesthesia. By explaining the process clearly and addressing concerns, anesthetists help patients feel more at ease.
The Importance of Anesthetists in Patient Safety
Patient safety is at the heart of anesthetic practice. Anesthetists are responsible for ensuring that anesthesia is administered in a controlled and secure environment. This involves sterilisation of equipment, precise measurement of medication, and vigilant monitoring throughout the procedure. Their quick interventions can prevent or manage complications such as allergic reactions, breathing issues, or sudden drops in blood pressure.
Anesthetists in Different Medical Specialties
Anesthetists work across various medical fields, adapting their skills to different situations:
Surgical Anesthesia: Supporting operations in general surgery, orthopedics, neurosurgery, and cardiac surgery.
Obstetric Anesthesia: Managing pain during labour and delivery, including epidural analgesia.
Pediatric Anesthesia: Providing safe anesthesia for infants and children, requiring specialised training and gentle care.
Critical Care: Overseeing patients in intensive care units who need sedation or pain control.
Pain Medicine: Offering chronic pain management for conditions such as arthritis, nerve pain, or cancer-related discomfort.
Preoperative and Postoperative Care
The work of an anesthetist begins long before surgery and continues well after it ends. Preoperatively, they assess the patient’s readiness for anesthesia, order necessary tests, and discuss the anesthesia plan. Postoperatively, they manage pain through medications, nerve blocks, or patient-controlled analgesia. They also watch for complications and guide patients through recovery, ensuring a smooth transition back to normal activities.
Technological Advancements in Anesthetics
Modern anesthesia benefits from cutting-edge technology that enhances safety and comfort. Advanced patient monitoring systems allow anesthetists to track vital functions with unmatched accuracy. Computer-assisted drug delivery systems ensure precise dosing, while improved anesthetic agents provide faster recovery times and fewer side effects. These innovations, combined with the expertise of an anesthetist, have made modern surgery safer and more efficient than ever before.
The Human Side of Anesthesia
While anesthesia is rooted in science, it also requires a deep understanding of patient psychology. Many individuals approach surgery with fear and uncertainty. Anesthetists play a crucial role in providing reassurance, explaining procedures clearly, and ensuring the patient feels supported. This compassionate approach builds trust and reduces anxiety, which can lead to smoother recoveries.
The Future of Anesthetic Practice
The field of anesthetic medicine continues to evolve, with ongoing research focusing on safer drugs, more accurate monitoring systems, and personalised anesthesia plans based on genetic and biometric data. As medical procedures become more advanced, the role of anesthetists will remain essential, ensuring that patient safety and comfort are never compromised.