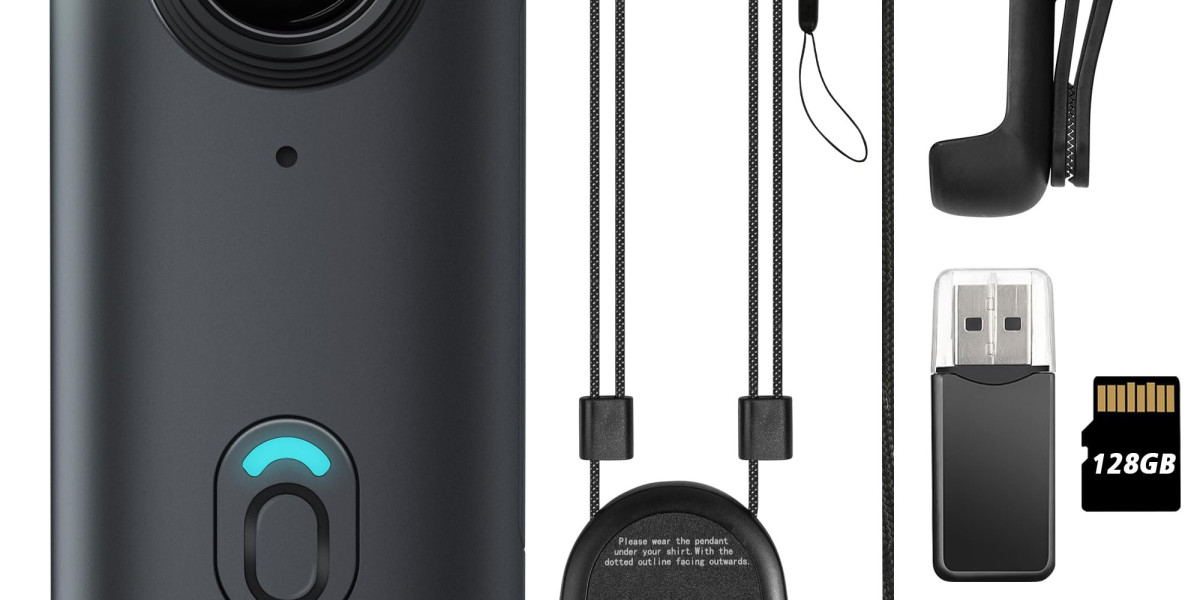
The wearable camera market is being disrupted on multiple fronts as technology advances, user behaviors evolve, and regulatory frameworks tighten. What was once a niche gadget category is now at the center of sweeping changes impacting everything from product functionality to data management and user ethics.
AI-Powered Intelligence Creating New Use-Cases
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming wearable cameras from passive recording devices into intelligent vision tools. Features like real-time facial recognition, object detection, and automatic scene tagging are becoming core differentiators. This disruption is allowing the technology to expand into areas such as autonomous surveillance, smart training tools, and predictive safety alerts.
AI-driven disruption has opened new enterprise applications, including construction site monitoring, law enforcement body cameras with bias detection, and healthcare wearables that flag procedural anomalies.
Privacy Regulations Forcing Rethink in Design
Tighter data privacy laws like the GDPR and California’s CCPA are forcing manufacturers to embed privacy-first design into their hardware and software. This shift is not just technical—it is market disruptive. Companies must re-architect storage, consent management, and facial data processing, which is altering production cycles and competitive timelines.
These compliance hurdles are encouraging the growth of on-device processing and encrypted edge storage, minimizing reliance on external servers.
Consumer Shift from Ownership to Access
The rise of subscription-based and cloud-linked wearable cameras is disrupting traditional hardware ownership models. Consumers and businesses increasingly favor access to upgraded services—like cloud storage, AI-based editing, and analytics—instead of purchasing expensive standalone devices.
This "camera-as-a-service" approach is redefining revenue models and encouraging bundling with broader ecosystems like home automation or mobile content platforms.
Platform Lock-In and Ecosystem Wars
Platform fragmentation is a major disruption point. Wearable cameras that only function optimally within proprietary ecosystems (e.g., Apple HealthKit, Amazon Alexa, or Meta platforms) are creating walled gardens. Users are forced to choose hardware based on ecosystem compatibility rather than specs alone.
This dynamic is pushing manufacturers to either go all-in on a closed-loop strategy or risk being commoditized in the open-access market.
Disruption in Distribution and Sales Channels
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) models and online marketplaces are replacing traditional retail channels for wearable cameras. Niche players now launch globally through crowdfunding platforms or e-commerce giants, bypassing conventional distributors. This democratization of access is disrupting brand hierarchies and allowing faster market entry for startups.
At the same time, enterprise sales are increasingly managed through specialized solution integrators and technology consultants rather than broad electronics resellers.
Convergence with Augmented Reality Devices
The overlap between wearable cameras and AR devices is creating a major point of disruption. Smart glasses with embedded cameras, voice commands, and real-time data overlays are gradually merging categories. This convergence is forcing traditional camera manufacturers to rethink their product boundaries and partner with AR/VR solution providers.
Companies that fail to adapt may lose relevance as multifunctional wearables dominate.
Crisis-Driven Demand Surges Creating Supply Tensions
Unpredictable spikes in demand due to social unrest, pandemics, or political surveillance initiatives are disrupting supply chains. During such periods, wearable cameras are suddenly in high demand for frontline workers, journalists, and law enforcement—resulting in temporary shortages and expedited feature rollouts that may bypass thorough testing.
These scenarios reveal market fragility and the need for better resilience planning.
Open-Source and Modular Disruption
A growing community of open-source hardware developers is introducing modular wearable camera designs. These offer customizable components, from lenses to chips, and encourage rapid prototyping. Though still nascent, this movement could disrupt the current mass-manufacturing model and give rise to local, customizable production at scale.
If widely adopted, it could revolutionize how cameras are made and deployed in education, local journalism, and DIY content creation.
Behavioral Disruption: Always-On Recording Culture
The normalization of constant personal recording is facing social and ethical backlash. As wearable cameras become smaller and more discreet, they blur the line between personal expression and surveillance. This cultural shift is disrupting public behavior, legal interpretations of consent, and acceptable norms in social spaces.
Governments and organizations are now re-evaluating where and how such devices may be used, leading to fluctuating demand in regulated environments.
Conclusion
The wearable camera market is experiencing a multi-layered disruption that touches product design, legal structures, user expectations, and monetization. From AI and platform dependencies to shifting behaviors and privacy laws, companies must stay agile to remain competitive. As these forces intensify, only adaptable, ethical, and tech-forward brands will thrive in the new market landscape