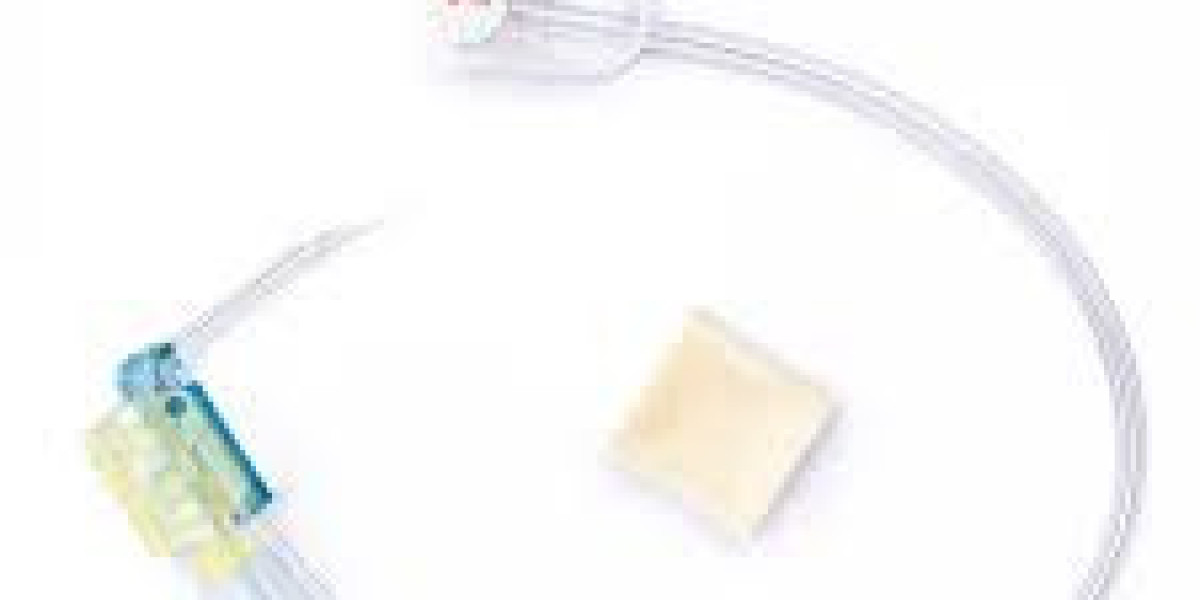
The huber needles market continues to evolve with a growing emphasis on enhancing patient and clinician safety. As healthcare systems worldwide prioritize infection prevention, occupational protection, and procedural excellence, the design and use of Huber needles are adapting accordingly. To explore thorough analysis, forecasts, and safety-driven innovations, the full huber needles market report is available.
Below, we examine key patient safety trends shaping the industry, as well as their impact on product design, regulatory expectations, and clinical outcomes.
1. Adoption of Safety‑Engineered Needle Features
A major patient safety trend in the Huber needle space is the widespread adoption of safety-engineered designs. Modern models feature:
Automatic shielding technology that encapsulates the needle tip immediately after use to prevent accidental stick injuries.
Active or passive locking systems, securing the needle in a safe position post-removal.
Self-blunting or retractable tips, further minimizing risk of clinician exposure.
These mechanisms help protect healthcare workers from occupational hazards while also supporting safer handling in home-based or outpatient settings.
2. Enhanced Non‑Coring and Bevel Precision
Precision design advances aim to protect patients by reducing device-related trauma. Improvements include:
Ultra-polished beveled tips that glide smoothly through port septa.
Optimized bevel angles, minimizing coring of silicone membranes.
Consistent insertion force, reducing discomfort and port wear.
The cumulative effect is greater durability of implantable ports, less trauma during repeated access, and reduced risk of infection or port failure over time.
3. Infection Control Focus
Patient safety extends to preventing infections associated with port access. Recent safety trends include:
Antimicrobial coatings applied to hubs or needle surfaces to inhibit bacterial colonization.
Sterile single-use packaging that meets rigorous infection prevention protocols.
Tamper-evident wrap or sealing, maintaining product integrity from shipment to use.
These measures are especially critical for immunocompromised patients undergoing long-term infusion therapies.
4. Human-Centered Ergonomic Design
Human-centered design is central to improving safety during insertion procedures. Safety-centric enhancements include:
Wider, textured wings for slip-resistant control.
Color-coded hubs and gauge indicators to reduce selection and handling errors.
Insertion depth markings, helping avoid accidental deep penetration.
By reducing user fatigue and procedural mistakes, ergonomic improvements drive safer, more consistent clinical outcomes.
5. Training, Simulation & Education
A key component of patient safety trends involves strengthening clinician competency. Industry players now offer:
Simulation platforms allowing safe, repeated needle insertion practice.
Standard training modules and certification programs, improving global port-access consistency.
Instructional materials in multiple languages, tailored to home caregivers and remote users.
Regulated training ensures proper technique and correct use of safety features, which is essential for both patient and clinician protection.
6. Traceability and Recall Management
Enhanced traceability features help maintain safety when product issues arise:
Batch-level lot coding and barcodes ensure rapid identification of affected units.
Integration with hospital EMR systems, capturing needle use data and supporting incident reporting.
Digital recall notification systems that link usage logs, audit history, and inventory control.
These traceability practices ensure swift action in case of recalls or adverse event investigations.
7. Home Infusion Safety Protocols
As more patients receive infusion therapy at home, ports and Huber needles are used outside clinical supervision. Safety measures now include:
Simplified packaging and labeling to minimize handling errors.
Self-blunting or shielded tip designs, reducing risk if needles are improperly handled.
Telehealth or mobile app–based oversight, providing virtual guidance for insertion and removal.
These innovations help mitigate risks associated with non-clinical environments and empower patients or caregivers to administer treatment safely.
8. Mini-Kits Tailored for Patient Use
New offerings include pre-assembled procedure kits designed for home care:
Needles paired with extension tubing, antiseptic swabs, and dressing, all in a single sterile pack.
Patient-friendly instructions with visual cues and easy-to-follow steps.
Single-use disposables, reducing cross-contamination risks.
These kits improve compliance with sterile technique while simplifying the experience for non-professional users.
9. Compatibility & Standardization Protocols
To support safe device use, there is growing demand for standardized compatibility:
Uniform needle-to-port interfacing to avoid mismatched components.
Universal depth and gauge labeling, making selection easier and safer.
Standardized color-coding systems, improving consistency across manufacturers.
Standardization reduces handling errors and prevents complications arising from incompatible equipment.
10. Environmental & Safety-Conscious Packaging
Beyond device safety, packaging strategy plays a role in safe use:
Tamper-evident seals that guarantee sterility up to point of opening.
Easy-tear sterile wrappers, minimizing contamination risk upon access.
Single-dose blister packaging, reducing handling and cross-contamination in busy settings.
Appropriate packaging enhances safety across product storage and use phases.
Impacts on Market and Clinical Practice
Manufacturers obligated to incorporate safety innovations in standard offerings.
Healthcare facilities benefit from fewer needlestick injuries and procedural complications.
Clinicians and caregivers gain confidence and clarity in use, promoting safer practice.
Patients experience fewer complications, longer port device longevity, and safer infusion experiences.
Conclusion
Patient safety trends in the huber needles market demonstrate a clear shift toward safer designs, infection control, ergonomic use, and traceable handling. From professional healthcare settings to remote home care scenarios, innovations such as safety shielding, antimicrobial coatings, ergonomic markers, and tele-training support are redefining safety standards.
As patient-centric care models and home-based infusion therapy expand, patient safety will remain a core driver of product design and market differentiation. Industry leaders who prioritize smarter, safer Huber needle solutions are poised to deliver better clinical outcomes and build trust across providers and users globally.