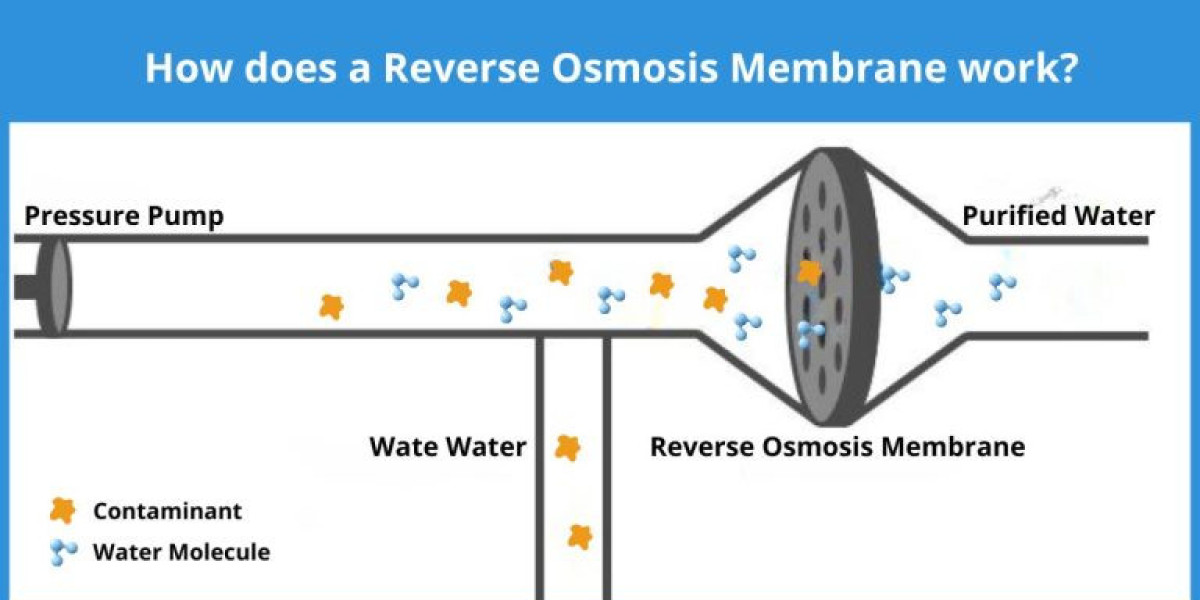
The Reverse Osmosis Membrane Market is pivotal in addressing global water scarcity, yet it faces multiple hindrances that slow its adoption and technological progress. These obstacles impact manufacturers, project developers, and end-users, creating both operational and financial challenges.
One major hindrance is the high upfront capital requirement for installing RO systems. While operational costs can be optimized over time, initial expenditures for membranes, housing units, pumps, and related infrastructure deter adoption, especially in developing regions with limited funding.
Technical hindrances also play a role. Issues like membrane fouling, scaling, and biofilm growth not only lower efficiency but also require frequent maintenance. This increases downtime and adds to the total cost of ownership for end-users such as municipalities and industries.
The energy demands of RO systems remain a persistent barrier. Despite improvements in membrane permeability and energy recovery devices, desalination and water purification still require significant power, making operations costly in energy-constrained areas.
Regulatory and environmental constraints further slow adoption. Strict rules regarding brine disposal, chemical use, and discharge standards can delay project approvals or require costly compliance measures, particularly in regions with evolving environmental legislation.
Supply chain disruptions have also emerged as a hindrance. Shortages in raw materials, transportation delays, and geopolitical uncertainties can impact the timely availability of membranes and related components, delaying project timelines.
Addressing these hindrances will require targeted innovations such as longer-lasting, low-maintenance membranes, improved pretreatment solutions, and policies that encourage investment in water infrastructure. Strategic partnerships between technology providers, governments, and funding agencies will be crucial to overcoming these barriers.